Industrial Laser Safety Officer Certification
What are the requirements to become a Laser Safety Officer?
Industrial LSO Certification - $149
With our curriculum, you will become the in-house expert in the following:
- How Lasers Propagate Light
- Scientific Terms
- Hazard Evaluation
- Control Measures
- Medical Examinations
- Non-Beam Hazards
- Eye & Skin Exposure
- Protective Equipment
LSO General Requirements
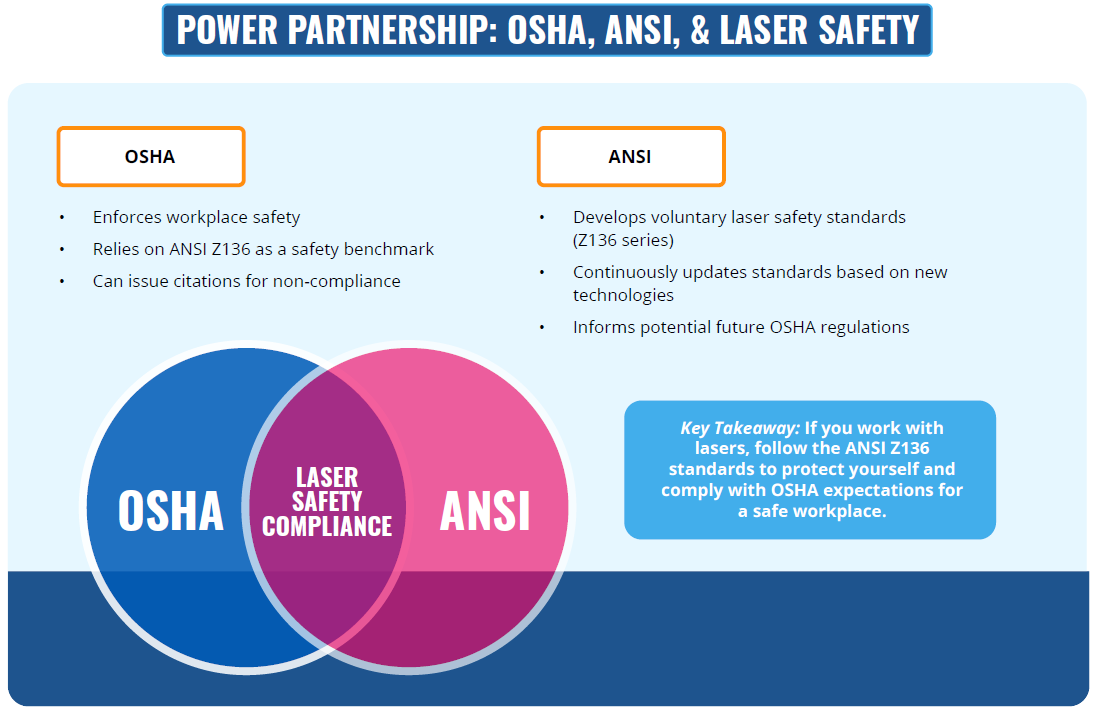
ANSI Z136 Standards
ANSI Z136.1 – Safe Use of Lasers:
- ANSI Z136.1 is the primary standard for laser safety, covering the use of lasers in various environments including research, manufacturing, and healthcare.
- It provides guidelines on hazard classification, control measures, and safety protocols.
- It defines the roles and responsibilities of the Laser Safety Officer (LSO) and specifies the requirements for training, signage, and personal protective equipment (PPE).
ANSI Z136.3 – Safe Use of Lasers in Health Care:
- ANSI Z136.3 is specific to the use of lasers in healthcare settings such as hospitals, dental offices, and clinics.
- It addresses the unique challenges and safety considerations of medical laser use, including procedural controls and patient safety measures.
- It also outlines the responsibilities of healthcare providers and the LSO in maintaining a safe environment.
OSHA Regulations
OSHA Standards:
- OSHA provides guidelines and regulations to ensure workplace safety, including the use of lasers.
- The OSHA Technical Manual (OTM), particularly Section III, Chapter 6, provides detailed information on laser safety standards and best practices.
- OSHA regulations require employers to implement safety programs, provide training, and ensure proper control measures are in place for laser operations.
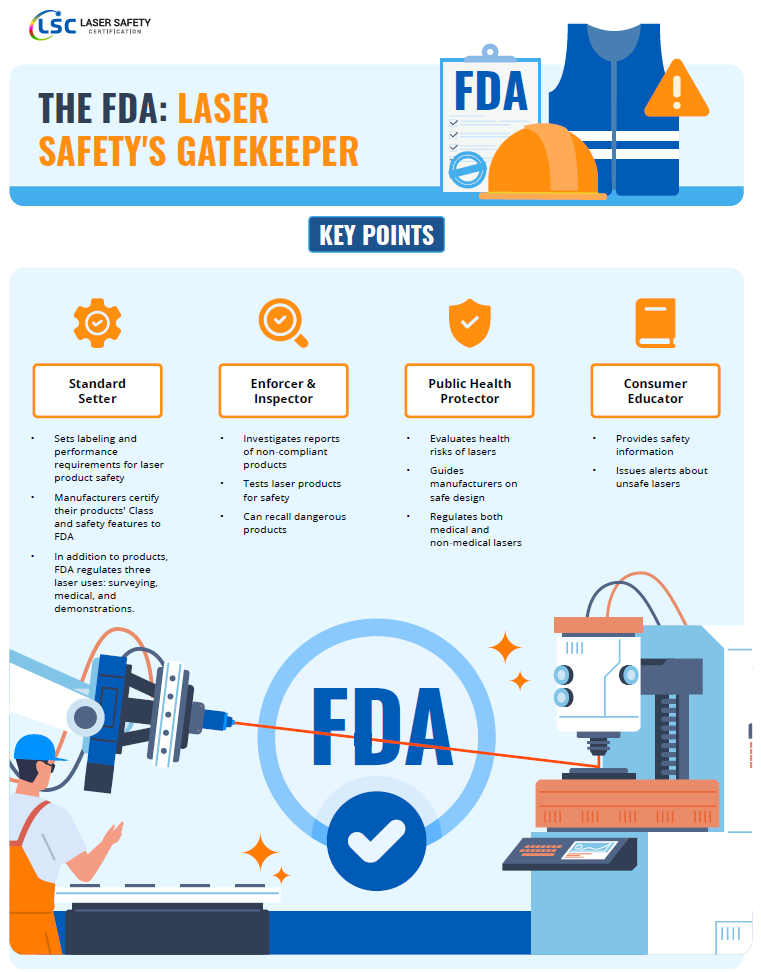
FDA Regulations
Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH):
- The FDA’s CDRH regulates the manufacturing and performance standards for lasers and laser systems.
- It ensures that lasers sold in the United States meet specific safety standards, including labeling, performance, and reporting requirements.
- The CDRH also oversees the classification of lasers based on their potential hazard.
State and Local Regulations
State-Specific Regulations:
- Many states have their own laser safety regulations that may be more stringent than federal guidelines.
- These regulations often require registration of laser systems, licensing of operators, and regular inspections.
- LSOs must be aware of and comply with these state-specific requirements in addition to federal standards.
Key Components of the Standards
Laser Classification:
- Lasers are classified based on their potential to cause harm, with classes ranging from Class 1 (low risk) to Class 4 (high risk).
- The classification determines the level of control measures required.
Control Measures:
- Engineering Controls: These include safety features built into the laser system, such as interlocks, beam enclosures, and warning systems.
- Administrative Controls: These involve policies and procedures, including training programs, safety protocols, and operational guidelines.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Includes laser safety goggles, gloves, and protective clothing.
Hazard Evaluation:
- LSOs must evaluate the work environment and laser systems to identify potential hazards and implement appropriate safety measures.
- This includes defining the Nominal Hazard Zone (NHZ) and ensuring proper labeling and signage.
Training and Education:
- Regular training programs must be provided to all personnel who may be exposed to laser hazards.
- Training should cover the fundamentals of laser safety, specific operational procedures, and emergency response protocols.
What are the standards that regulate laser safety?
To become a Laser Safety Officer (LSO), several requirements and responsibilities must be met. Based on the provided documents, we discussed key requirements and responsibilities.
By meeting these requirements and fulfilling these responsibilities, an individual can effectively serve as a Laser Safety Officer, ensuring the safe use of lasers within their organization.
These standards and regulations work together to create a comprehensive framework for laser safety. By following the guidelines set forth in ANSI Z136 standards, OSHA regulations, FDA requirements, and state-specific rules, organizations can ensure the safe use of lasers and protect their employees from potential hazards.